E Class|Can you tell the difference between RGV and AGV? This article will clarify it for you
May 31,2023
Summary
Many beginners in the logistics industry are often confused by various product terms. Before this, we have introduced the definition and concept of stacker, WMS, AGV and other products for you. In this article, we will continue to bring you another important and easily confused equipment RGV with AGV, explain its development, function, characteristics and the difference between them.
Many beginners in the logistics industry are often confused by various product terms. Before this, we have introduced the definition and concept of stacker, WMS, AGV and other products for you. In this article, we will continue to bring you another important and easily confused equipment RGV with AGV, explain its development, function, characteristics and the difference between them.

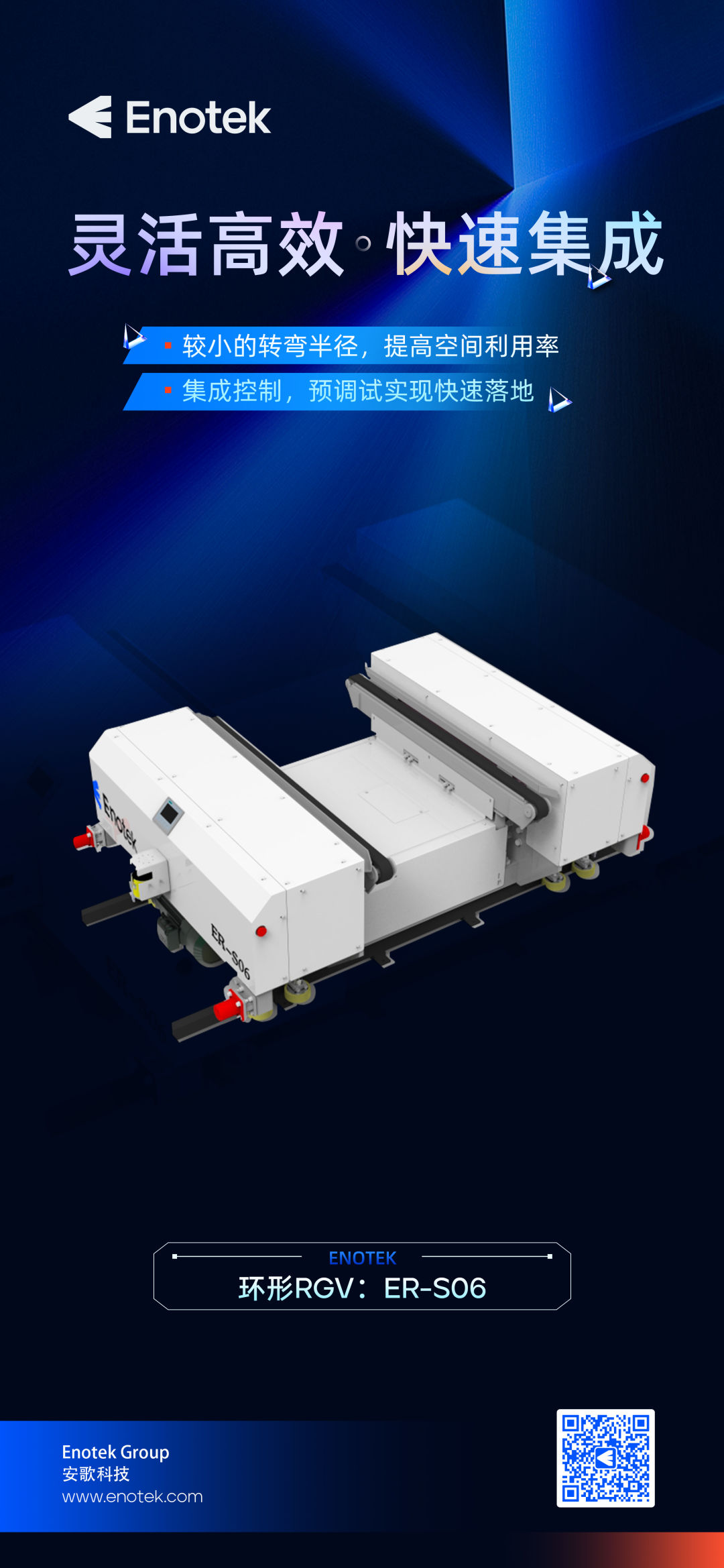
RGV (Rail Guided Vehicle), also known as automated guided vehicle, is a type of robot used for automated logistics transport. It typically uses sensors, navigation systems and control systems to sense the surrounding environment, plan routes and perform tasks, which can improve logistics efficiency, reduce manual labor and errors, and improve operational flexibility and accuracy.
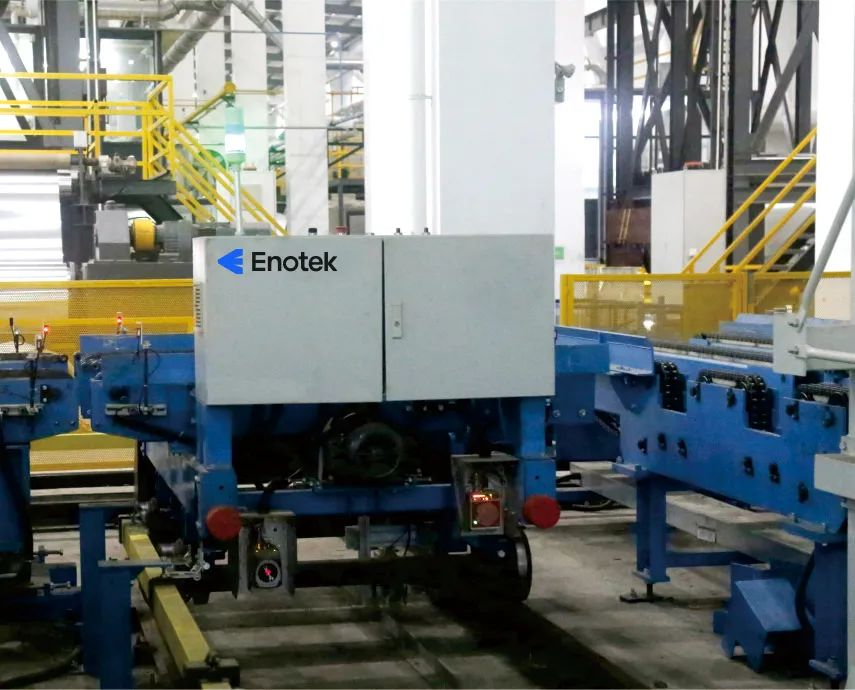

They usually use technology such as guide rail, tape or laser navigation to navigate, and can carry different types of vehicles or jigs to move different types and sizes of items as required. RGVS play an important role in modern logistics and manufacturing.

Early development: In the 1950s and 1960s, RGV technology began to be used commercially. At that time, RGVS were mainly used in the field of industrial automation, carrying out material transportation and handling on the production line.
Guideway navigation system: In the early stage of development, RGV mostly adopts the guideway navigation system. By laying guideways on the ground, the robot can travel along the specified path, which is suitable for carrying out repetitive transportation tasks in a fixed area.
Introduction of autonomous navigation technology: With the continuous development of navigation technology, autonomous navigation RGV began to rise. Using technologies such as sensors, lasers, vision and navigation algorithms, RGVS can sense their environment, locate and plan optimal paths in real time, enabling autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance.

Expansion of applications: In addition to traditional industrial manufacturing, the growing RGVS are also widely used in warehousing logistics, health care, retail and other fields. They can be used for automated warehouse cargo handling, drug distribution, material replenishment and other tasks.
Multifunctional vehicles and increased flexibility: Modern RGVS can not only move cargo, but also be equipped with a variety of vehicles and clamps to accommodate different item types and sizes, enabling multiple functions of RGVS in different scenarios and missions.
Collaboration and networking: With the development of Industry 4.0 and Internet of Things technology, RGVS can collaborate and network with other devices and systems. By connecting with robots, sensors and central control systems, RGVS can achieve higher levels of automation and intelligence.

Load capacity: Generally, RGVS have a relatively high load capacity and can handle heavy cargo and materials. AGVs typically have light load capacity and are suitable for smaller items and light logistics operations.
Application scenario: The RGVs rely on guidance cables or navigation belts for positioning. RGVs are applicable to fixed routes, repetitive tasks, and scenarios that require high path accuracy, such as material handling on production lines. AGVs are applicable to scenarios that require more flexible path planning, greater adaptability, and collaboration with other automated devices, such as storage and transportation of goods in warehouses.
System complexity: The RGV system is relatively simple. It usually uses the wired guidance mode and only needs to be laid and maintained. AGV systems are more complex and require the use of more advanced navigation techniques, such as laser navigation or visual navigation. These technologies involve more sensors and algorithms, increasing the complexity of the system.
Vehicle population and size: Since RGVs are typically navigated via fixed guidance lines, conflicts and coordination problems can arise when multiple RGVs operate on the same guidance line. As a result, AGVs can better enable multi-vehicle collaboration and smooth logistics operations when automated guidance vehicles are needed on a large scale.
Adaptability and scope of application: RGVs are usually suitable for relatively stable and fixed production lines or logistics scenarios. AGVs are more adaptable. They can adapt to different environments and layouts, and can perform more complex tasks, such as path planning, obstacle avoidance and autonomous decision-making.
In general, RGVs are more suitable for relatively simple and fixed logistics scenarios, such as material transportation on production lines. AGVs are suitable for more flexible, complex and large-scale logistics and warehousing operations, such as cargo handling, sorting and storage in warehouses. Whether to choose AGV or RGV depends on the specific application scenario.
After reading today's article, do you also have a more comprehensive understanding of RGV? If you want to learn more logistics knowledge, please follow us Wechat. In addition to E class, we also have E Insight focusing on the forefront of the industry, E Craftsman telling the story of logistics people, and E meaning of three-minute popular science short video, please pay attention to us!












